All about Input Tax Credit
Last udpated: Nov. 4, 2017, 9:12 p.m.To avoid cascading effect governments all over the world provide input tax credit. Under GST also input tax credit is available which can be utilised to pay against tax liability of output tax.
Before proceeding to input tax credit provisions, first understand some terms and logic behind input tax credit.
GST is an indirect tax, which is levied at each stage of product or service supplied. If we charge tax on entire bill amount without providing relief of tax already paid towards inward supplies, then it will result in multiple taxation and tax will be levied on tax already suffered.
What is Cascading effect of taxes?
Definition of cascading effect can be explained as a tax on tax. When tax is charged on taxes already paid under the same act, this is called as cascading effect.
For example, if you have purchased a product for and paid tax under GST. Again when you sell the product, if you are including the input tax as a part of your cost and charge tax on it then it becomes a cascading taxing.
Below image explains the cascading effect.
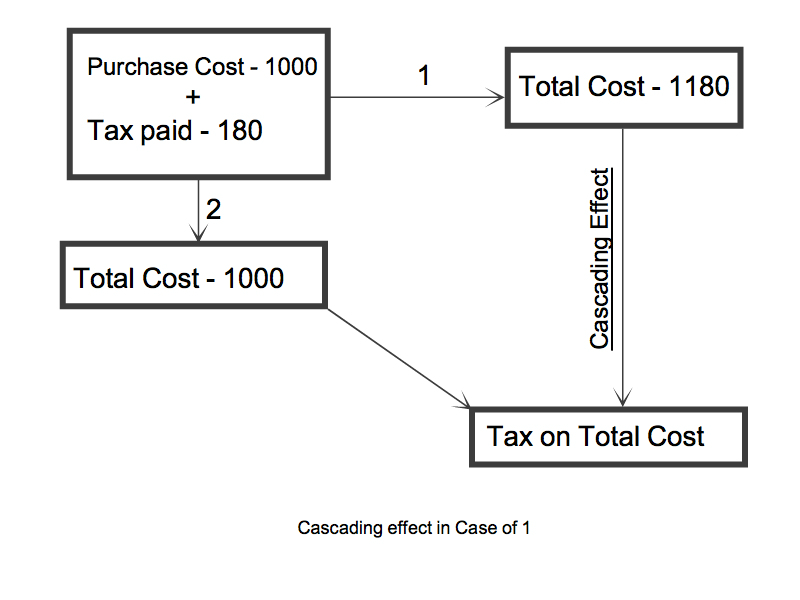 Here you can notice that in 1st transaction, buyer has considered tax charged on purchase as a part of cost and when this product is further sold he pays tax on tax already paid at the time of purchase.
Here you can notice that in 1st transaction, buyer has considered tax charged on purchase as a part of cost and when this product is further sold he pays tax on tax already paid at the time of purchase.
What is Input Tax and what is input tax credit?
Definition of input tax is any tax paid on the goods or services purchased. If your sales are taxed under GST, then whatever GST you will pay on purchase of products or services will be your input tax.
Input tax credit means credit of input tax.
Section 2 of CGST Act defined input tax as:

In a simple language input tax is tax paid under different GST acts on inward supplies.
Eligibility to avail input tax credit
Every person who is registered under GST is allowed to take credit of input tax charged on any supply of goods or services or both if they were used for in the business.
Input tax credit will be allowed only if you have:
- Tax invoice or any other document specified under act issued by supplier
- Actually received the goods or services or both.
Further the supplier should have paid the tax to government either in cash or through input credit utilisation and also should have filed the return under section 39.
If you do not pay the invoice amount to supplier within 180 days then input tax credit availed should be added back to you output tax liability. This can be afterwards availed when you pay the amount to supplier.
If you have claimed input tax as part of cost for taking depreciation under Income Tax Act, then you can not avail the credit of input tax paid.
Further the input tax credit can be availed only before filing the return for the month of September after year end or filing of annual return whichever is earlier.
Input tax credit on supplies used partly for taxable supplies and partly for exempted or personal purpose
If you are using the goods or services or both partially for taxable outward supplies and partially for exempt supplies or for personal use then input tax credit should be taken only for the amount attributable to the taxable outward supply.
The rules for apportionment are yet to be notified and apportionment have to be made as per rules prescribed by government with this regard.
Inward supplies on which input tax credit is not available
Input tax credit cannot be taken on certain supplies of goods or services or both. Section 17 of CGST Act, specifies the list of supplies on which credit cannot be taken.
Credit can not be availed on motor vehicles and other conveyances except when they are used for:
- Making taxable supplies
- Further in course of business
- Transportation of passengers or
- Used for training on driving, flying, navigating such vehicles or conveyances.
- For transportation of goods.
Further on following supply of goods or services or both input tax credit is not available:
- Food and beverages,
- Outdoor catering,
- Beauty treatment,
- Health services,
- Cosmetic and plastic surgery
However if these are further supplied outwards as a taxable supply then input is allowed.
- Membership of a club or health and fitness centre,
- Renting a cab, life insurance and health insurance,
- Travel benefits to employees such LTA,
- Supplies on construction of immovable property except plant and machinery
- Supplies procured from a supplier paying tax under composition scheme
- Goods which are lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or given for free as a gift or sample
- Goods on which tax is recovered by officers under the act.
The common thing should be noted that input is allowed if these supplies are further used in supply of taxable supplies.
I will write a different post on:
- Availing input credit in different situations such as:
- Goods lying as on the date of registration,
- Goods lying at the time of conversion from composition levy to normal tax levy
- Where exempted supplies become taxable
- Selling of fixed assets
- In case of mergers and amalgamations
- Input tax on goods sent for job-work
You need to be logged in to comment.
- Free Tools
- Verify GST Number
- Search GST Number with name or pan
- Search Multiple GST numbers
- Search Multiple PAN numbers
- Top Members
- Related
- Annual Returns under GST
- KNOW SOME INDIRECT TAXES NOT SUBSUMED IN GST
- DENIAL OF CREDIT/DEBIT OF ELECTRONIC CREDIT LEDGER UNDER RULE 86A OF CGST RULES
- All About GSTR2B
- UNDERSTANDING ON SEC-8, CGST ACT
- UNDERSTANDING ON Sec-9 CGST ACT
- UNDERSTANDING ON Sec-7 CGST ACT
- 6 digit HSN code or 4 digit HSN code
- Proposed Amendment in Sec: 16 vide Finance Bill, 2021
- E-Invoice in GST
Never File Wrong GSTR-1
Check your GST numbers in bulk. Check unlimited GST numbers with very cheap packages.
Used by













2 Comments
how to download this app
Which App? Invoicing application?
IT is online application. No need to download. Use it online.